Thinking Like an Attacker: The Power of Threat Modeling in Software Development
Thinking Like an Attacker: The Power of Threat Modeling in Software Development...
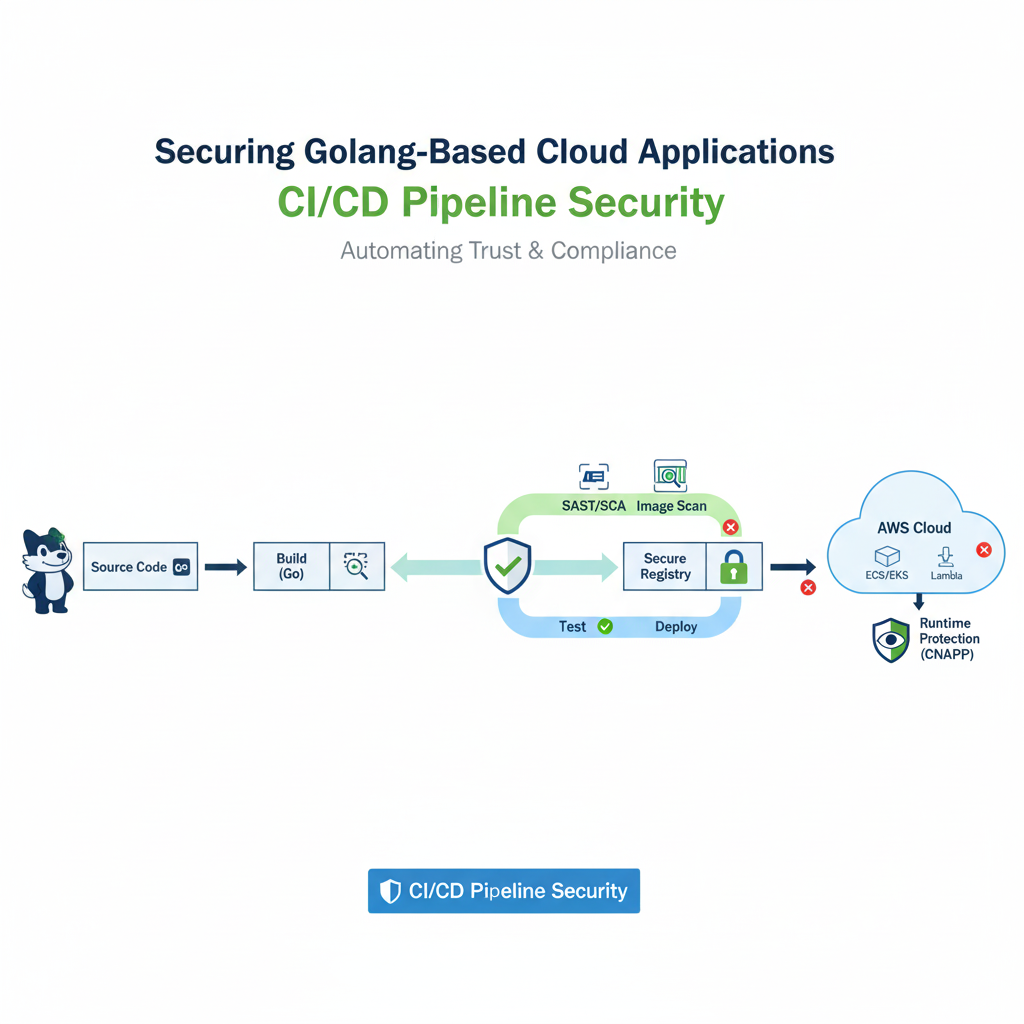
As the software development landscape evolves, one of the biggest concerns developers face today is ensuring that their applications are secure, especially when they are deployed in cloud environments. The CI/CD pipeline (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) has become the backbone of modern development workflows, automating the build, test, and deployment processes. However, with the increased speed of development, securing the CI/CD pipeline has become critical in protecting against vulnerabilities, data leaks, and other security threats.
In this blog, we will explore how to secure your Golang-based cloud applications within the CI/CD pipeline, offering best practices and tools to keep your applications secure from development through deployment.
The CI/CD pipeline automates the process of building, testing, and deploying code, providing faster feedback loops and allowing developers to ship updates more quickly. A typical CI/CD pipeline consists of:
Continuous Integration (CI): The process of automatically building and testing code changes that are pushed to the version control system (like Git).
Continuous Deployment (CD): The process of automatically deploying those tested changes to production or staging environments.
However, this automation also introduces risks. Without a well-secured pipeline, vulnerabilities can be introduced during each phase of development and deployment. Securing the CI/CD pipeline ensures that every stage from development to production is safeguarded against potential threats.
The first line of defense in securing a Golang-based cloud application is to ensure that the code itself is secure before it is even built or deployed. This involves conducting static code analysis to identify vulnerabilities early in the development cycle.
Best practices for static code analysis in Golang:
Use tools like GoSec to scan your codebase for potential security flaws, such as SQL injections, XSS, or command injection
vulnerabilities.
Integrate SonarQube into your CI pipeline to automatically perform static code analysis on every code commit, providing feedback to developers about vulnerabilities or code quality issues.
Consider using Golang linters (e.g., golint, gosec, gofmt) to ensure code consistency and spot potential issues that could be exploited.
By incorporating static analysis into your CI pipeline, you ensure that vulnerabilities are flagged and resolved before the code is built or tested.
Third-party libraries and dependencies are often a source of vulnerabilities, and this is no different for Golang applications. Ensuring that your dependencies are free from known vulnerabilities should be a critical step in your CI/CD pipeline.
Best practices for dependency security:
Go modules: If you're using Go modules (introduced in Go 1.11), ensure that you're always working with the latest stable versions of dependencies. Use go get to update outdated dependencies.
Use a tool like Dependabot to automatically check for outdated or vulnerable dependencies in your Golang project.
Incorporate a tool like Snyk or Trivy into your CI pipeline to scan your dependencies for known vulnerabilities. Snyk specifically works well with Go to detect and fix security issues in open-source packages.
By checking for vulnerable dependencies during the CI phase, you can prevent dependency confusion attacks, supply chain vulnerabilities, and other issues from affecting your application.
Storing sensitive information such as API keys, database credentials, or environment variables in plaintext is a serious security risk. Secrets should never be hardcoded into your codebase or stored insecurely in version control systems.
Best practices for secrets management:
Use HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, or Google Cloud Secret Manager to store and manage sensitive data securely. These tools provide encrypted storage and access control for secrets.
Integrate your CI/CD pipeline with secrets management tools so that sensitive data can be retrieved dynamically during deployment without being exposed in source code.
Environment variables should be used to pass secrets into containers at runtime. This ensures that secrets are never part of the codebase, and are only available when needed.
If your Golang applications are being deployed in containers, ensuring the security of the container images is paramount. Containers can inherit vulnerabilities from the base image, making it crucial to scan your images for vulnerabilities before deploying them to the cloud.
Best practices for container security:
Use Trivy, an open-source vulnerability scanner for containers, to scan your Docker images for known vulnerabilities. Trivy integrates well with CI/CD pipelines and supports multiple container image registries.
Integrate Clair or Anchore into your pipeline for continuous vulnerability scanning of container images.
Always base your container images on official or trusted base images, and avoid using unverified third-party images.
Regularly update your container images to ensure that they are running the latest, most secure versions of dependencies.
Access control is crucial in ensuring that only authorized individuals and services can interact with the cloud infrastructure. Properly managing Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles and policies is critical for minimizing the risk of data breaches.
Best practices for IAM security:
Use role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure that only the necessary team members have access to sensitive environments, and limit access to production to a smaller, more secure group.
Leverage least-privilege access to reduce the risk of internal threats and unauthorized access. Ensure that each service or person has the minimum level of access needed to perform their job.
Automate the process of rotating keys and access tokens within the CI/CD pipeline to avoid long-lived credentials that can be compromised.
Even after your Golang application is deployed, ongoing security monitoring is essential to detect any malicious activity or performance anomalies. Implement logging and monitoring systems to track application behavior in production.
Best practices for monitoring:
Use tools like Prometheus and Grafana for monitoring metrics related to application health and security.
Implement AWS CloudWatch, Google Stackdriver, or other logging solutions to centralize logs from various sources (such as Kubernetes, containers, or application logs).
Integrate security-focused monitoring tools, such as Falco or Aqua Security, to detect unusual activities in containerized environments and Kubernetes clusters.
Securing your Golang-based cloud applications within the CI/CD pipeline is critical to preventing vulnerabilities from slipping through into production. By implementing static code analysis, securing your dependencies, using proper secrets management, and automating container vulnerability scans, you can greatly reduce the risk of security breaches. Additionally, enforcing strict IAM policies and continuously monitoring production environments ensures that your applications stay secure over time.